Why do we start with liver support in our clinic?
The liver is one of the most vital organs in the human body, performing over 500 functions essential to maintaining overall health. A healthy liver is key in processing nutrients, filtering toxins, and regulating biochemical processes that sustain life. Understanding its functions and role in detoxification highlights why liver health is crucial for overall wellness.
Key Functions of the Liver
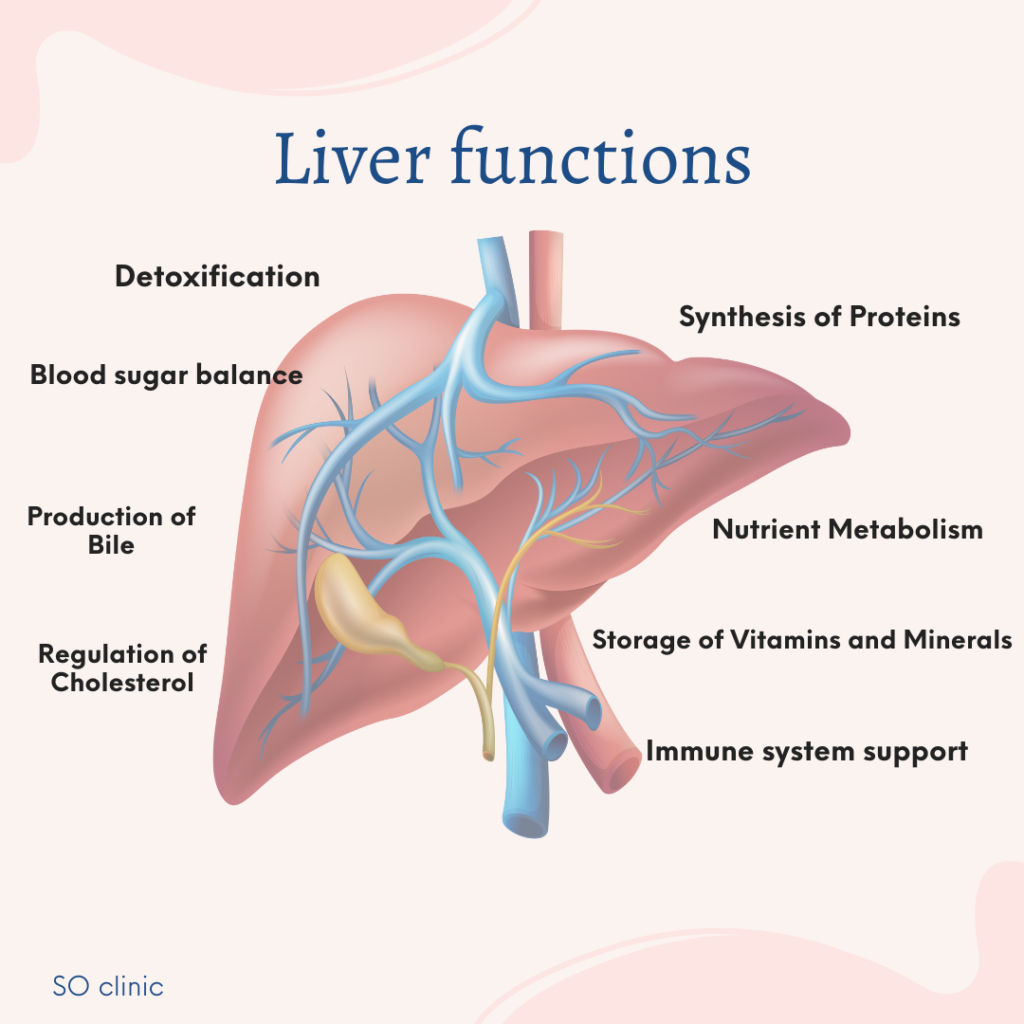
1. Detoxification
The liver is primarily known for its ability to detoxify harmful substances. Every day, your body is exposed to toxins—whether
from food, medication, alcohol, environmental pollutants, or even the natural byproducts of metabolism. The liver filters these toxins from the blood and processes them for elimination, ensuring they do not accumulate. Without the liver’s detoxifying role, toxins would overwhelm
the body, leading to dieseases.
2. Nutrient Metabolism
One of the liver’s essential tasks is metabolising nutrients. After food is digested in the stomach and intestines, the nutrients are transported to the liver via the bloodstream. The liver processes carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, converting them into energy
or storing them. For instance, it stores glucose as glycogen and releases it when the body requires energy, helping maintain blood sugar levels.
3. Production of Bile
Bile is a digestive fluid produced by the liver that is essential for the breakdown and absorption of fats. The liver continuously produces bile, which is stored in the gallbladder and released into the small intestine during digestion. This process not only helps in the digestion of
fats but also the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K.
4. Synthesis of Proteins
The liver is responsible for synthesising many critical proteins in the body. One of the most important is albumin, which helps maintain blood volume and pressure by keeping fluid within the blood vessels. The liver also produces clotting factors that are essential for
stopping bleeding when injuries occur.
5. Regulation of Cholesterol
The liver plays a central role in regulating cholesterol levels. It produces cholesterol, which is necessary for the synthesis of hormones and the production of cell membranes. Additionally, the liver converts excess cholesterol into bile salts, which are used in digestion or excreted, thereby helping maintain balanced cholesterol levels.
6. Storage of Vitamins and Minerals
The liver is a storage hub for essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamins A, D, E, K, and B12, as well as iron and copper. These nutrients are stored until the body needs them for various physiological functions.
The Liver and Detoxification
The detoxification process in the liver involves two primary phases—Phase 1
and Phase 2 detoxification.
1. Phase 1 Detoxification: Modification
In Phase 1, liver enzymes known as cytochrome P450 enzymes modify toxins, drugs, and other harmful substances. This modification process prepares these compounds for Phase 2 by making them more reactive. While Phase 1 detoxifies many substances, it also produces intermediate compounds that can be even more toxic than the original substances. These compounds are immediately passed on to Phase 2 to be neutralised.
2. Phase 2 Detoxification: Conjugation
Phase 2 is known as the conjugation phase. During this phase, the liver neutralises the reactive and toxic intermediates produced in Phase 1 by binding them to water-soluble molecules, such as glutathione, sulfur, or amino acids. This process renders the compounds non-toxic, allowing them to be excreted through urine or bile.
This two-step detoxification system works continuously to protect the body from toxic overload. Maintaining liver health ensures this process functions efficiently, reducing the risk of toxin accumulation and associated health issues.
Supporting Liver Health
Maintaining a healthy liver is crucial, given its extensive role in detoxification, energy production, digestion, and more. Here are a few ways to support liver function:
Eat a Nutrient-Dense Diet:
Fruits and vegetables are rich in antioxidants that support liver detoxification. Cruciferous vegetables (like broccoli, kale, and cauliflower) contain compounds that enhance liver enzyme activity.
Limit Alcohol Consumption:
Alcohol places a heavy burden on the liver, impairing its ability to detoxify and regenerate. Limiting alcohol intake can significantly support liver health.
Stay Hydrated:
Adequate water intake helps flush toxins out of the body through urine and supports the liver’s detoxifying processes.
Exercise Regularly:
Physical activity enhances circulation, aids liver detoxification, and promotes weight management, reducing strain on the liver.
Consider Herbal Support:
Herbs like milk thistle, dandelion root, and turmeric have been shown to support liver health by enhancing detoxification and promoting liver cell regeneration.